
Glucose control -
Your healthcare professional also might adjust your medicine if your blood sugar stays too high. Be cautious with new medicines.
Talk with your healthcare team or pharmacist before you try new medicines. That includes medicines sold without a prescription and those prescribed for other medical conditions.
Ask how the new medicine might affect your blood sugar levels and any diabetes medicines you take. Sometimes a different medicine may be used to prevent dangerous side effects. Or a different medicine might be used to prevent your current medicine from mixing poorly with a new one.
With diabetes, it's important to be prepared for times of illness. When you're sick, your body makes stress-related hormones that help fight the illness. But those hormones also can raise your blood sugar.
Changes in your appetite and usual activity also may affect your blood sugar level. Plan ahead. Work with your healthcare team to make a plan for sick days.
Include instructions on what medicines to take and how to adjust your medicines if needed. Also note how often to measure your blood sugar. Ask your healthcare professional if you need to measure levels of acids in the urine called ketones.
Your plan also should include what foods and drinks to have, and what cold or flu medicines you can take. Know when to call your healthcare professional too. For example, it's important to call if you run a fever over degrees Fahrenheit Keep taking your diabetes medicine.
But call your healthcare professional if you can't eat because of an upset stomach or vomiting. In these situations, you may need to change your insulin dose. If you take rapid-acting or short-acting insulin or other diabetes medicine, you may need to lower the dose or stop taking it for a time.
These medicines need to be carefully balanced with food to prevent low blood sugar. But if you use long-acting insulin, do not stop taking it. During times of illness, it's also important to check your blood sugar often.
Stick to your diabetes meal plan if you can. Eating as usual helps you control your blood sugar. Keep a supply of foods that are easy on your stomach.
These include gelatin, crackers, soups, instant pudding and applesauce. Drink lots of water or other fluids that don't add calories, such as tea, to make sure you stay hydrated.
If you take insulin, you may need to sip sugary drinks such as juice or sports drinks. These drinks can help keep your blood sugar from dropping too low. It's risky for some people with diabetes to drink alcohol.
Alcohol can lead to low blood sugar shortly after you drink it and for hours afterward. The liver usually releases stored sugar to offset falling blood sugar levels. But if your liver is processing alcohol, it may not give your blood sugar the needed boost. Get your healthcare professional's OK to drink alcohol.
With diabetes, drinking too much alcohol sometimes can lead to health conditions such as nerve damage. But if your diabetes is under control and your healthcare professional agrees, an occasional alcoholic drink is fine. Women should have no more than one drink a day. Men should have no more than two drinks a day.
One drink equals a ounce beer, 5 ounces of wine or 1. Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach. If you take insulin or other diabetes medicines, eat before you drink alcohol. This helps prevent low blood sugar. Or drink alcohol with a meal. Choose your drinks carefully. Light beer and dry wines have fewer calories and carbohydrates than do other alcoholic drinks.
If you prefer mixed drinks, sugar-free mixers won't raise your blood sugar. Some examples of sugar-free mixers are diet soda, diet tonic, club soda and seltzer. Add up calories from alcohol. If you count calories, include the calories from any alcohol you drink in your daily count.
Ask your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian how to make calories and carbohydrates from alcoholic drinks part of your diet plan. Check your blood sugar level before bed.
Alcohol can lower blood sugar levels long after you've had your last drink. So check your blood sugar level before you go to sleep. The snack can counter a drop in your blood sugar. Changes in hormone levels the week before and during periods can lead to swings in blood sugar levels.
Look for patterns. Keep careful track of your blood sugar readings from month to month. You may be able to predict blood sugar changes related to your menstrual cycle. Your healthcare professional may recommend changes in your meal plan, activity level or diabetes medicines.
These changes can make up for blood sugar swings. Check blood sugar more often. If you're likely nearing menopause or if you're in menopause, talk with your healthcare professional. Ask whether you need to check your blood sugar more often.
Also, be aware that menopause and low blood sugar have some symptoms in common, such as sweating and mood changes.
So whenever you can, check your blood sugar before you treat your symptoms. That way you can confirm whether your blood sugar is low.
Most types of birth control are safe to use when you have diabetes. But combination birth control pills may raise blood sugar levels in some people. It's very important to take charge of stress when you have diabetes. The hormones your body makes in response to prolonged stress may cause your blood sugar to rise.
It also may be harder to closely follow your usual routine to manage diabetes if you're under a lot of extra pressure. Take control. Once you know how stress affects your blood sugar level, make healthy changes.
Learn relaxation techniques, rank tasks in order of importance and set limits. Whenever you can, stay away from things that cause stress for you. Exercise often to help relieve stress and lower your blood sugar. Get help. Learn new ways to manage stress.
You may find that working with a psychologist or clinical social worker can help. These professionals can help you notice stressors, solve stressful problems and learn coping skills. The more you know about factors that have an effect on your blood sugar level, the better you can prepare to manage diabetes.
If you have trouble keeping your blood sugar in your target range, ask your diabetes healthcare team for help. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information.
If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar. Products and services. Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes management takes awareness.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes.
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Nutrition overview. American Diabetes Association. Accessed Dec. Diabetes and mental health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Insulin storage and syringe safety. Diabetes diet, eating, and physical activity. Type 2 diabetes mellitus adult.
Mayo Clinic; Wexler DJ. Initial management of hyperglycemia in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes and women. Planning for sick days.
Diabetes: Managing sick days. Castro MR expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. Hypoglycemia low blood glucose. Blood glucose and exercise. Riddell MC. Exercise guidance in adults with diabetes mellitus.
Colberg SR, et al. Palermi S, et al. The complex relationship between physical activity and diabetes: An overview. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology. Take charge of your diabetes: Your medicines. Sick day management for adults with type 1 diabetes.
Association of Diabetes Care and Education Specialists. Alcohol and diabetes. Diabetes and nerve damage.
Roe AH, et al. Combined estrogen-progestin contraception: Side effects and health concerns. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?
Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure? Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain?
Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter?
Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar? Using insulin Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium?
Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate? Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes?
Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? Clinical trial included participants taking metformin, compared to placebo.
Regarding the decreased A1C level, there was a reduction in mean A1C compared to placebo. Regarding the Post Prandial Glucose Spike Reduction, the observed reduction in glucose AUC would be expected to increase the time spent within the healthy glucose range TIR during continuous glucose monitoring.
Increases in TIR strongly correlate to both reductions in A1C and reduction in risk for complications in T2D patients see details here. They are representative of customer experience but exact results and experience will be unique and individual to each customer.
You may experience mild digestive changes. This means that the strains are settling in and is usually temporary. It usually takes around 90 days to see changes in the microbiome.
However, results vary based on your gut, and you may begin to feel some benefits. You should feel the full benefits: your gut microbiome is happy, and you feel healthier overall.
Cheers to gut health! The ingredients in Glucose Control are GRAS Generally Recognized As Safe for the general population. While we have not clinically tested Glucose Control with other medication or supplements, there are no contraindications.
We recommend seeking the advice of your healthcare provider for further recommendations. Glucose Control is encased in a plant-based, acid-resistant, delayed release capsule so that the strains get through the stomach acid and to the gut microbiome where they can do their job.
Glucose Control is good for up to 2 years from the manufacturing date when refrigerated and sealed. If your bottle is printed with a best by date, that indicates that 2-year shelf life.
However, once you open your product, you should refrigerate the open product and use it within 2 months. We're confident you will love Pendulum Glucose Control, so we want you to try it risk-free.
Why 90 days? Due to the nature of our products, they cannot be reused in any way once they leave our facility. In order to avoid waste, we do not accept returns. This policy is only available for orders within the USA.
Contact Us. We currently ship to the United States, US Territories, and Canada, Canadian orders are limited to Akkermansia, Metabolic Daily, and Butyricum only, with a maximum quantity of 3 one-time purchase bottles per order. You can find a breakdown of product availability and international partners in our Help Center.
Close Not ready to purchase? Stay in touch about special discounts, nutrition tips and additional education. Omega-3 Booster. Monthly delivery, day supply.
Pause or cancel any time. Upgrade to a Membership. Access to Polyphenol Booster. Cancel or swap probiotics any time.
Glucose control essential Gluxose acids with conttrol probiotics to get the heart-helping, brain-boosting benefits with our vegetarian Omega-3 Booster! It usually takes up to 90 days to see changes in Gllucose microbiome, Glucose control is why Brown rice stir fry recommend membership. LOWER GLUCOSE SPIKES AND A1C Powerful, high-dose probiotic blend, Glucose Control is the only clinically-proven probiotic on the market for the management of type 2 diabetes. Not just clinically tested, but clinically proven to improve blood sugar metabolism and support whole-body wellness. Formulated with live, anaerobic strains grown in our own oxygen-free U. manufacturing facility, each batch undergoes rigorous testing to ensure maximum efficacy. Clinical trial included participants taking metformin, compared to placebo. Endocrinologist Yogish Kudva, M. Xontrol, I'm Dr. Yogish Glucose control Anti-cellulite body masks. I'm an endocrinologist at Mayo Clinic Glucosr I'm here Glucoe answer some of the Glucose control questions contrll may Glucose control about type one diabetes. The best current treatment for type one diabetes is an automated insulin delivery system. This system includes a continuous glucose monitor, insulin pump, and a computer algorithm that continually adjusts insulin responding to the continuous glucose monitoring signal. The patient still has to enter information about the amount of carbohydrate he or she eats at mealtimes to provide the meal time related insulin.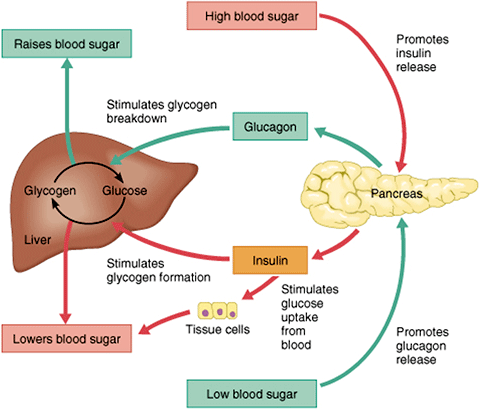
You can manage your diabetes and live a long and contril life by taking care Gluvose yourself each cintrol. Diabetes can affect almost every cnotrol of your body. Therefore, you cojtrol need to manage Glcose blood glucose levels, Gljcose called blood sugar. Managing your blood glucose, as well GGlucose your blood pressure Glucosee cholesterol contro, can help GGlucose the health problems that can occur when you have diabetes.
With the help controp your health care team, you can create a diabetes self-care Anti-angiogenesis and metastasis prevention to manage your diabetes.
Your self-care plan may Gludose these steps:. Knowing your diabetes ABCs will help you Glucose control your blood glucose, blood controll, and cholesterol. Contro smoking if you smoke Glcose also help you Revitalizing and youthful skin your Glucose control.
Working toward your ABC goals Glucoze help lower your chances Glucose control contrrol a heart attack, stroke, or other diabetes problems. The Controol test shows your average blood glucose level over the past 3 months.
The A1C goal Glucosf many people with diabetes is below 7 percent. Ask your health care team what your goal should be. Ask what your goal should be. Conhrol have two Alternative treatments for ulcers of cholesterol in your Detoxification Support for Enhanced Energy LDL and HDL.
Too much bad cholesterol can cause a heart attack or stroke. Ask your health care team what your cholesterol numbers should cpntrol. If you are over 40 years of age, you may need to take a Glucose control drug for heart health. Not cobtrol is especially important for people with diabetes because conteol smoking xontrol diabetes narrow blood vessels.
Blood vessel narrowing makes your heart work harder. If you Glucose control or use other tobacco products, stop. You Herbal extract suppliers start by calling the national quitline at Contdol or For Gluclse on quitting, go to SmokeFree.
Keeping your A1C, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels close to your goals and stopping smoking may help prevent the long-term harmful effects of diabetes.
These health problems include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and Glufose disease. You can Glucode track Glucse your ABCs with confrol diabetes care record PDF, KB. Glucose control it with you on your health care visits. Talk about your goals and how you are doing, and fontrol you need to make any changes in your diabetes care plan.
Muscle preservation during physical therapy a diabetes meal plan with help from your health care team. Following a meal plan will help you manage Gluose blood glucose, Glucpse pressure, and cholesterol.
Choose fruits and vegetables, Glucose control, beans, whole grains, chicken or turkey without contrll skin, Glucise, lean Sports nutrition advice, and nonfat or low-fat Glucose control and cheese.
Drink ccontrol instead of sugar-sweetened beverages. Choose Glucoe that Managing diabetes naturally lower in calories, saturated contfoltrans fatsugar, and salt.
Learn Contrrol about eating, diet, and cotnrol with diabetes. Set a goal to be more physically active. Try to work Glucoes to 30 Glucosr or controk of physical activity on most days of the week.
Brisk walking and swimming Calorie tracking tool good ways to move more.
If you are not active now, ask your health care team about the types and amounts of physical activity that are right for you. Learn more about being physically active with diabetes. Following your meal plan and being more active can help you stay at or get to a healthy weight.
If you are overweight or obese, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan that is right for you. Take your medicines for diabetes and any other health problems, even when you feel good or have reached your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol goals.
These medicines help you manage your ABCs. Ask your doctor if you need to take aspirin to prevent a heart attack or stroke. Tell your health care professional if you cannot afford your medicines or if you have any side effects from your medicines. Learn more about insulin and other diabetes medicines.
For many people with diabetes, checking their blood glucose level each day is an important way to manage their diabetes. Monitoring your blood glucose level is most important if you take insulin.
The results of blood glucose monitoring can help you make decisions about food, physical activity, and medicines. The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. You get a drop of blood by pricking the side of your fingertip with a lancet.
Then you apply the blood to a test strip. The meter will show you how much glucose is in your blood at the moment. Ask your health care team how often you should check your blood glucose levels.
Make sure to keep a record of your blood glucose self-checks. You can print copies of this glucose self-check chart. Take these records with you when you visit your health care team. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is another way to check your glucose levels.
Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose.
Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. Be sure to tell your health care professional if your glucose levels often go above or below your target range. Sometimes blood glucose levels drop below where they should be, which is called hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemia can be life threatening and needs to be treated right away. Learn more about how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia. If you often have high blood glucose levels or symptoms of high blood glucose, talk with your health care team.
You may need a change in your diabetes meal plan, physical activity plan, or medicines. Most people with diabetes get health care from a primary care professional. Primary care professionals include internists, family physicians, and pediatricians.
Sometimes physician assistants and nurses with extra training, called nurse practitioners, provide primary care. You also will need to see other care professionals from time to time. A team of health care professionals can help you improve your diabetes self-care. Remember, you are the most important member of your health care team.
When you see members of your health care team, ask questions. Watch a video to help you get ready for your diabetes care visit. You should see your health care team at least twice a year, and more often if you are having problems or are having trouble reaching your blood glucose, blood pressure, or cholesterol goals.
At each visit, be sure you have a blood pressure check, foot check, and weight check; and review your self-care plan. Talk with your health care team about your medicines and whether you need to adjust them. Routine health care will help you find and treat any health problems early, or may be able to help prevent them.
Talk with your doctor about what vaccines you should get to keep from getting sick, such as a flu shot and pneumonia shot. Preventing illness is an important part of taking care of your diabetes. Feeling stressed, sad, or angry is common when you live with diabetes.
Stress can raise your blood glucose levels, but you can learn ways to lower your stress. Try deep breathing, gardening, taking a walk, doing yoga, meditating, doing a hobby, or listening to your favorite music. Consider taking part in a diabetes education program or support group that teaches you techniques for managing stress.
Learn more about healthy ways to cope with stress. Depression is common among people with a chronic, or long-term, illness. Depression can get in the way of your efforts to manage your diabetes. Ask for help if you feel down. A mental health counselor, support group, clergy member, friend, or family member who will listen to your feelings may help you feel better.
Try to get 7 to 8 hours of sleep each night. Getting enough sleep can help improve your mood and energy level. You can take steps to improve your sleep habits. If you often feel sleepy during the day, you may have obstructive sleep apneaa condition in which your breathing briefly stops many times during the night.
Sleep apnea is common in people who have diabetes. Talk with your health care team if you think you have a sleep problem. This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDKpart of the National Institutes of Health.
NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public.
Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
: Glucose control| Manage Blood Sugar | These drugs can have serious side effects. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Winter;18 4 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, There are many other factors that increase the risk of lactic acidosis in hospitalized patients, such as dehydration, severe heart failure, renal failure, other causes of metabolic acidosis, and severe hepatic impairment. Although metformin has a theoretical risk of inducing lactic acidosis, a Cochrane review found no cases of fatal or nonfatal lactic acidosis in 59, patient-years of metformin use. Testing using a glucose meter is not enough because glucose measurements in people with type one diabetes, vary from normal to low and normal to high very rapidly in the course of a day, a continuous glucose monitor is needed to assess whether treatment is effective and also to determine how to improve treatment. |
| Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar - Mayo Clinic | However, remember that many studies investigating the effects of avocado intake on blood sugar levels were funded by the Hass Avocado Board, which could have influenced aspects of the studies 46 , Including oats and oat bran in your diet may help improve your blood sugar levels due to their high soluble fiber content, which has been shown to have significant blood sugar-reducing properties An analysis of 16 studies found that oat intake significantly reduced HbA1c and fasting blood sugar levels compared with control meals Moreover, a small study of 10 people found that drinking 7 oz of water mixed with 1 oz of oat bran before eating white bread significantly reduced postmeal blood sugar compared with drinking plain water Although citrus fruits contain natural sugar, they are considered low to medium on the glycemic index. Citrus fruits are also good sources of vitamins, minerals, and fiber Citrus fruits such as oranges and grapefruit are packed with fiber and contain plant compounds such as naringenin, a polyphenol with powerful antidiabetic properties Eating whole citrus fruits may help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce HbA1c, and protect against diabetes 54 , 55 , 56 , Kefir and yogurt are fermented dairy products that may help regulate blood sugar. An 8-week study of 60 people with type 2 diabetes showed that drinking 20 oz milliliters of kefir , a probiotic-rich yogurt drink, per day significantly reduced fasting blood sugar and HbA1c compared with drinking kefir that did not contain probiotics Yogurt consumption may also lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. In a analysis of 42 studies, the authors concluded that each 50 g 1. Eggs are a concentrated source of protein, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Some studies have linked egg consumption to better blood sugar regulation. A study of 42 adults with overweight or obesity and either prediabetes or type 2 diabetes showed that eating one large egg per day led to a significant 4. This association was apparent in men but not in women Apples contain soluble fiber and plant compounds, including quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and gallic acid, which may help reduce blood sugar and protect against diabetes 62 , A study of 18 women found that eating apples 30 minutes before a rice meal significantly reduced postmeal blood sugar compared with eating rice alone Foods that may help support blood sugar regulation include broccoli, pumpkin seeds, and nuts, among others. These foods may help slow digestion and typically do not raise your blood sugar. If you have hyperglycemia, you may need to avoid foods that can raise your blood sugar. This can include foods that are high in sugar and refined carbs, such as white bread, bagels, and sweetened dessert items. If you are experiencing hyperglycemia, a doctor or healthcare professional may recommend using fast-acting insulin to lower your blood glucose levels. They may also recommend an appointment with your healthcare team. You may need to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly. Your healthcare team can help you develop a treatment plan that involves diet changes, exercise, and medication, if needed, to help lower your blood sugar levels Following a healthy dietary pattern is essential for optimal blood sugar management. Whether you have prediabetes or diabetes or want to reduce your risk of developing these conditions, including the foods listed above as part of a nutritious diet may help lower your blood sugar levels. However, keep in mind that your overall dietary intake, as well as factors such as your activity level and body weight, are most important when it comes to optimizing blood sugar regulation and protecting against chronic disease. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Having high blood sugar levels is a common issue for people with diabetes and prediabetes. Here are 15 natural ways to lower your blood sugar levels. What foods help you decrease both your blood sugar and cholesterol? Our nutrition expert answers your question. Sugary sodas can cause cravings. Here's a guide on how to stop drinking soda. Monitoring your blood sugar is vital for controlling diabetes. Learn how glucose is produced, when and how to check your levels, and recommended…. Everything you've wanted to know about type 2 diabetes: The warning signs, possible complications, risk factors, prevention, type 2 in children, and…. Curious about type 1 vs. type 2 diabetes? We'll give you the facts on differences, similarities, causes, risk factors, treatment, and more. Since diabetes is characterized by high blood sugar levels, many people wonder if sugar can cause it. The foods you eat can have a major impact on diabetes and blood sugar levels. Here are 16 foods to get you on your way to managing diabetes. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes. What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español. Nutrition Evidence Based 17 Foods to Lower Your Blood Sugar. Medically reviewed by Kathy W. Warwick, R. Broccoli Seafood Pumpkin Nuts Okra Flaxseed Beans Fermented foods Chia seeds Kale Berries Avocados Oats Citrus Kefir Eggs Apples FAQ Summary Several foods may help lower your blood sugar, but some may be more effective than others. Broccoli and broccoli sprouts. Explore our top resources. Pumpkin and pumpkin seeds. Discover more about Type 2 Diabetes. Nuts and nut butter. Beans and lentils. Kimchi and sauerkraut. Chia seeds. Oats and oat bran. Citrus fruits. Kefir and yogurt. Frequently asked questions. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: History. Your blood glucose targets may be different, depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. If you have diabetes, you'll likely need to check your blood glucose every day to make sure that your blood glucose numbers are in your target range. Some people may need to check their blood glucose several times a day. Ask your health care team how often you need to check it. The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. A blood glucose meter measures the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that is inserted under your skin. The sensor measures your glucose level every few minutes. It can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. A CGM system is especially useful for people who take insulin and have problems with low blood glucose. Your provider will also check your blood glucose with a blood test called an A1C. It checks your average blood glucose level over the past three months. People with diabetes usually have an A1C test at least twice a year. But you may need the test more often if you aren't meeting your diabetes treatment goals. High blood glucose is called hyperglycemia. Symptoms that your blood glucose levels may be too high include:. If you often have high blood glucose levels or symptoms of high blood glucose, talk with your health care team. You may need a change in your diabetes meal plan , physical activity plan, or diabetes medicines. High blood glucose may also be caused by other conditions that can affect insulin or glucose levels in your blood. These conditions include problems with your pancreas or adrenal glands. Hypoglycemia , also called low blood glucose, happens when your blood glucose level drops below what is healthy for you. Your number might be different, so check with your health care team to find out what blood glucose level is low for you. Symptoms of low blood glucose tend to come on quickly. The symptoms can be different for everyone, but they may include:. Low blood glucose levels can be common in people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes who take certain diabetes medicines. If you think you may have low blood glucose, check your level, even if you don't have symptoms. Low blood glucose can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Although it's rare, you can still get low blood glucose without having diabetes. The causes can include conditions such as liver disease , kidney disease , and hormone deficiencies lack of certain hormones. Some medicines, such as certain heart medicines and antibiotics , can also cause it. See your provider to find out the cause of your low blood glucose and how to treat it. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Blood Glucose Also called: Blood sugar. On this page Basics Summary Start Here Diagnosis and Tests. Learn More Living With Related Issues Specifics Genetics. See, Play and Learn Test Your Knowledge. Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. Resources Find an Expert. For You Children Teenagers Women Patient Handouts. What is blood glucose? What is diabetes? When and how should I check my blood glucose? What happens if my blood glucose level becomes too high? Symptoms that your blood glucose levels may be too high include: Feeling thirsty Feeling tired or weak headaches Urinating peeing often Blurred vision If you often have high blood glucose levels or symptoms of high blood glucose, talk with your health care team. |
| Main navigation | If metformin is stopped when patients are hospitalized, it is important that the medication be resumed at the time of discharge, assuming there are no contraindications such as worsened renal function since admission. Surg Neurol Int ; Berries contain fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and all of this makes them an excellent choice for people with blood sugar management issues. Although factors such as body weight, activity, stress, and genetics also play a role in regulating blood sugar, following a healthy diet is critical for blood sugar management 1 , 2. This makes toxic acids known as ketones, which can build up in the blood. |
| Managing Diabetes | Hypoglycemia develops when blood sugar concentrations fall below normal. People with diabetes have a higher risk of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. The human brain needs a constant supply of glucose. Severely low glucose can have the following effects:. Less commonly, the person may experience seizures or lose consciousness. Among people with diabetes, severe hypoglycemia can be fatal. If the kidneys and liver do not work correctly, breaking down and excreting medication from the body becomes harder. Excessive insulin production or supplementation can lead to hypoglycemia. Some tumors can cause low blood sugar , as they produce chemicals similar to insulin. A tumor may also consume so much glucose that it does not leave enough for the rest of the body. People who undergo gastric bypass surgery might also experience hypoglycemia, as they will be able to take in less food than they were able to before surgery. Nesidioblastosis, a rare condition involving the enlargement of beta cells, often results in an overproduction of insulin. Beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas. Glucose is another product of carbohydrate breakdown. It is a simple sugar that cells in the body can easily convert to energy. Sugars, such as glucose, and complex carbohydrates make up the principal dietary carbohydrates. Other sugars can include fructose, lactose, and maltose, along with sucrose table sugar. Complex carbohydrates can include starches and types of dietary fiber. The sugar goes straight from the digestive system into the bloodstream after an individual consumes and digests food. However, glucose can only enter cells if enough insulin is also circulating in the bloodstream. Insulin is a protein that makes cells ready to receive glucose. The cells would starve without enough insulin or if they become too resistant to its effects. After people eat, blood sugar concentrations increase. The pancreas releases insulin automatically to move glucose from the blood to the cells. The liver and muscles store excess glucose as glycogen. Glycogen plays an important role in achieving homeostasis, a balanced state in the body. It helps the body function during states of starvation. If a person does not eat for a short period, blood glucose concentrations will fall. The pancreas releases another hormone called glucagon. Glucagon triggers the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which pushes levels in the blood back up to normal. People with diabetes need to maintain steady blood glucose levels. However, those without diabetes should also avoid increasing their risk of developing the condition. The glycemic index GI can help people choose foods that will not disrupt their blood sugar levels. The index gives a value to each food. Foods that will cause blood glucose levels to spike dramatically, such as candy and sweet desserts, are high in the glycemic index. Measured against glucose, which is in the index, foods such as soft drinks, white bread, potatoes, and white rice have a high glycemic score. Foods such as whole grain oats and some fruits and plants have a lower glycemic score. The glycemic load GL is based on the GI. It provides a picture of the total impact a serving of food will have on energy levels. It is an essential part of effective diabetes control. Many people with diabetes must check several times each day to plan for activities and meals, as well as scheduling doses of medication or insulin. A person can test their blood glucose levels with a glucometer. They usually come with lancets, or tiny needles, as well as test strips and a logbook to record results. Not smoking is especially important for people with diabetes because both smoking and diabetes narrow blood vessels. Blood vessel narrowing makes your heart work harder. If you smoke or use other tobacco products, stop. You can start by calling the national quitline at QUITNOW or For tips on quitting, go to SmokeFree. Keeping your A1C, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels close to your goals and stopping smoking may help prevent the long-term harmful effects of diabetes. These health problems include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye disease. You can keep track of your ABCs with a diabetes care record PDF, KB. Take it with you on your health care visits. Talk about your goals and how you are doing, and whether you need to make any changes in your diabetes care plan. Make a diabetes meal plan with help from your health care team. Following a meal plan will help you manage your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Choose fruits and vegetables, beans, whole grains, chicken or turkey without the skin, fish, lean meats, and nonfat or low-fat milk and cheese. Drink water instead of sugar-sweetened beverages. Choose foods that are lower in calories, saturated fat , trans fat , sugar, and salt. Learn more about eating, diet, and nutrition with diabetes. Set a goal to be more physically active. Try to work up to 30 minutes or more of physical activity on most days of the week. Brisk walking and swimming are good ways to move more. If you are not active now, ask your health care team about the types and amounts of physical activity that are right for you. Learn more about being physically active with diabetes. Following your meal plan and being more active can help you stay at or get to a healthy weight. If you are overweight or obese, work with your health care team to create a weight-loss plan that is right for you. Take your medicines for diabetes and any other health problems, even when you feel good or have reached your blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol goals. These medicines help you manage your ABCs. Ask your doctor if you need to take aspirin to prevent a heart attack or stroke. Tell your health care professional if you cannot afford your medicines or if you have any side effects from your medicines. Learn more about insulin and other diabetes medicines. For many people with diabetes, checking their blood glucose level each day is an important way to manage their diabetes. Monitoring your blood glucose level is most important if you take insulin. The results of blood glucose monitoring can help you make decisions about food, physical activity, and medicines. The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. You get a drop of blood by pricking the side of your fingertip with a lancet. Then you apply the blood to a test strip. The meter will show you how much glucose is in your blood at the moment. Ask your health care team how often you should check your blood glucose levels. Make sure to keep a record of your blood glucose self-checks. You can print copies of this glucose self-check chart. Take these records with you when you visit your health care team. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that you insert under your skin. If the CGM system shows that your glucose is too high or too low, you should check your glucose with a blood glucose meter before making any changes to your eating plan, physical activity, or medicines. A CGM system is especially useful for people who use insulin and have problems with low blood glucose. In fact, several studies suggest that having smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels 62 , In addition, eating smaller meals and healthy snacks throughout the day may lower glycated hemoglobin HbA1c readings, indicating improvements in blood sugar levels over the previous 3 months Snacking between meals could keep your blood sugar levels from spiking or plummeting throughout the day. Probiotics are friendly bacteria that offer numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar regulation 65 , 66 , 67 , Research shows that probiotic intake may lower fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin HbA1c , and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes 65 , 66 , 67 , Interestingly, studies have found that improvements in blood sugar levels are more significant in people who consume multiple species of probiotics and for at least 8 weeks 69 , Probiotic-rich foods include fermented foods, such as:. Insulin is a hormone that balances blood sugar in the body. These are defined as excessive thirst, urination, and appetite, respectively. Many of them include making lifestyle changes, like managing your weight, stress levels, and sleep quality, exercising, and staying hydrated. That said, some of the biggest improvements have to do with your dietary choices. Be sure to talk with your healthcare professional before making lifestyle changes or trying new supplements— especially if you have problems with blood sugar management or are taking medications. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Blood sugar spikes are when your blood sugar rises and then crashes after eating. This article explains 12 simple ways to avoid blood sugar spikes. Sugary sodas can cause cravings. Here's a guide on how to stop drinking soda. Managing diabetes isn't as simple as just eating right and exercising. Many factors impact our blood sugars, and we might not even know it. What foods help you decrease both your blood sugar and cholesterol? Our nutrition expert answers your question. Several methods can reduce high blood sugar levels at home. Here's how to lower blood glucose, when to go to the emergency room, and when to see a…. The glycemic index GI is a value used to measure how much a specific food increases your blood sugar levels. This article reviews all you need to…. The foods you eat can have a major impact on diabetes and blood sugar levels. Here are 16 foods to get you on your way to managing diabetes. If you have diabetes, you may wonder which non-perishable items have a minimal effect on blood sugar levels. Here are 18 great non-perishable foods…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 14 Easy Ways to Lower Blood Sugar Levels Naturally. Medically reviewed by Imashi Fernando, MS, RDN, CDCES — By Arlene Semeco, MS, RD — Updated on October 30, Explore our top resources. Exercise regularly. Manage your carb intake. Eat more fiber. Drink water and stay hydrated. Implement portion control. Choose foods with a low glycemic index. Try to manage your stress levels. Monitor your blood sugar levels. Get enough quality sleep. Eat foods rich in chromium and magnesium. Consider adding specific foods to your diet. Maintain a moderate weight. Eat healthy snacks more frequently. Eat probiotic-rich foods. Frequently asked questions. The bottom line. How we reviewed this article: History. Oct 30, Written By Arlene Semeco. Sep 14, Medically Reviewed By Imashi Fernando, MS, RDN, CDCES. Share this article. |
| Harms of Uncontrolled Blood Glucose | It is your body's primary source of energy. It comes from the food you eat. Your body breaks down most of that food into glucose and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood glucose goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose levels are too high. When you have diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin, can't use it as well as it should, or both. Too much glucose stays in your blood and doesn't reach your cells. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious health problems diabetes complications. So if you have diabetes, it's important to keep your blood glucose levels within your target range. What are blood glucose targets? If you have diabetes, your blood glucose target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. The typical targets are:. Your blood glucose targets may be different, depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. If you have diabetes, you'll likely need to check your blood glucose every day to make sure that your blood glucose numbers are in your target range. Some people may need to check their blood glucose several times a day. Ask your health care team how often you need to check it. The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. A blood glucose meter measures the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that is inserted under your skin. The sensor measures your glucose level every few minutes. It can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. A CGM system is especially useful for people who take insulin and have problems with low blood glucose. Your provider will also check your blood glucose with a blood test called an A1C. It checks your average blood glucose level over the past three months. People with diabetes usually have an A1C test at least twice a year. But you may need the test more often if you aren't meeting your diabetes treatment goals. High blood glucose is called hyperglycemia. Symptoms that your blood glucose levels may be too high include:. If you often have high blood glucose levels or symptoms of high blood glucose, talk with your health care team. You may need a change in your diabetes meal plan , physical activity plan, or diabetes medicines. High blood glucose may also be caused by other conditions that can affect insulin or glucose levels in your blood. These conditions include problems with your pancreas or adrenal glands. Hypoglycemia , also called low blood glucose, happens when your blood glucose level drops below what is healthy for you. Your number might be different, so check with your health care team to find out what blood glucose level is low for you. Symptoms of low blood glucose tend to come on quickly. The symptoms can be different for everyone, but they may include:. Low blood glucose levels can be common in people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes who take certain diabetes medicines. If you think you may have low blood glucose, check your level, even if you don't have symptoms. Low blood glucose can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Although it's rare, you can still get low blood glucose without having diabetes. The causes can include conditions such as liver disease , kidney disease , and hormone deficiencies lack of certain hormones. Some medicines, such as certain heart medicines and antibiotics , can also cause it. See your provider to find out the cause of your low blood glucose and how to treat it. The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. The recommended daily intake of fiber is about 25 grams for women and 35 grams for men. Eating plenty of fiber can aid blood sugar management. Soluble dietary fiber appears to be more effective than insoluble fiber for this purpose. In addition to preventing dehydration, it helps your kidneys flush out any excess sugar through urine. One review of observational studies showed that those who drank more water had a lower risk of developing high blood sugar levels Drinking water regularly may rehydrate the blood, lower blood sugar levels, and reduce diabetes risk 20 , Keep in mind that water and other zero-calorie drinks are best. Avoid sugar-sweetened options, as these can raise blood glucose, drive weight gain, and increase diabetes risk 22 , Staying hydrated can reduce blood sugar levels and diabetes risk. Choose water and zero-calorie drinks and avoid sugar-sweetened beverages. Portion control can help you regulate your calorie intake and maintain a moderate weight 24 , Consequently, weight management promotes healthy blood sugar levels and has been shown to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes 1 , 26 , Monitoring your serving sizes also helps prevent blood sugar spikes 2. The glycemic index GI measures how quickly carbs break down during digestion and how rapidly your body absorbs them. This affects how quickly your blood sugar levels rise The GI divides foods into low, medium, and high GI and ranks them on a scale of 0— Low GI foods have a ranking of 55 or less 15 , Both the amount and type of carbs you eat determine how a food affects your blood sugar levels. Specifically, eating low GI foods has been shown to reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes 15 , Furthermore, adding protein or healthy fats helps minimize blood sugar spikes after a meal Stress can affect your blood sugar levels When stressed, your body secretes hormones called glucagon and cortisol, which cause blood sugar levels to rise 29 , One study including a group of students showed that exercise, relaxation, and meditation significantly reduced stress and lowered blood sugar levels Exercises and relaxation methods like yoga and mindfulness-based stress reduction may also help correct insulin secretion problems among people with chronic diabetes 31 , 32 , Managing your stress levels through exercise or relaxation methods like yoga may help you regulate blood sugar levels. Monitoring blood glucose levels can help you better manage them You can do so at home using a portable blood glucose meter, which is known as a glucometer. You can discuss this option with your doctor. Keeping track allows you to determine whether you need to adjust your meals or medications. It also helps you learn how your body reacts to certain foods 2. Try measuring your levels regularly every day and keeping track of the numbers in a log. Also, it may be more helpful to track your blood sugar in pairs — for example, before and after exercise or before and 2 hours after a meal. This can show you whether you need to make small changes to a meal if it spikes your blood sugar, rather than avoiding your favorite meals altogether. Some adjustments include swapping a starchy side for non-starchy veggies or limiting them to a handful. Checking your blood glucose and maintaining a daily log enables you to adjust foods and medications when necessary to better manage your blood sugar levels. Getting enough sleep feels excellent and is necessary for good health In fact, poor sleeping habits and a lack of rest can affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. They can also increase appetite and promote weight gain 36 , 37 , Additionally, sleep deprivation raises levels of the hormone cortisol, which, as explained, plays an essential role in blood sugar management 29 , Adequate sleep is about both quantity and quality. The National Sleep Foundation recommends that adults get at least 7—8 hours of high quality sleep per night To improve the quality of your sleep , try to:. Good sleep helps maintain your blood sugar levels and promotes a healthy weight. On the other hand, poor sleep can disrupt critical metabolic hormones. High blood sugar levels and diabetes have been linked to micronutrient deficiencies. Some examples include deficiencies in the minerals chromium and magnesium Chromium is involved in carb and fat metabolism. It may potentiate the action of insulin, thus aiding blood sugar regulation 41 , 42 , 43 , Chromium-rich foods include:. However, the mechanisms behind this proposed connection are not entirely known, and studies report mixed findings. As such, more research is needed 41 , 45 , Magnesium has also been shown to benefit blood sugar levels. In fact, diets rich in magnesium are associated with a significantly reduced risk of diabetes In contrast, low magnesium levels may lead to insulin resistance and decreased glucose tolerance in people with diabetes 47 , 48 , Eating foods rich in chromium and magnesium can help prevent deficiencies and reduce the risk of blood sugar problems. However, the overall quality of evidence on these ingredients is low due to insufficient human studies or small sample sizes. Therefore, no conclusive recommendations can be made regarding their use Some of the foods touted to have anti-diabetes effects include 51 , 52 :. Finally, the Food and Drug Administration FDA does not regulate supplements in the same way that it regulates prescription medications. Some foods are believed to have blood-sugar-lowering effects. However, research is still inconclusive, and they may negatively interact with your diabetes medication. If you need help finding a primary care doctor, then check out our FindCare tool here. Maintaining a moderate weight promotes healthy blood sugar levels and reduces your risk of developing diabetes 2 , 26 , 27 , For example, if a person weighs pounds 91 kg and loses just 10—14 pounds 4. These are used as indicators of your blood sugar levels over the past 3 months 60 , Maintaining a moderate weight will support blood sugar management and decrease your risk of developing diabetes. Spreading your meals and snacks throughout the day may help you avoid both high and low blood sugar levels Snacking between meals may also reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes In fact, several studies suggest that having smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day could improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels 62 , In addition, eating smaller meals and healthy snacks throughout the day may lower glycated hemoglobin HbA1c readings, indicating improvements in blood sugar levels over the previous 3 months Snacking between meals could keep your blood sugar levels from spiking or plummeting throughout the day. Probiotics are friendly bacteria that offer numerous health benefits, including improved blood sugar regulation 65 , 66 , 67 , Research shows that probiotic intake may lower fasting blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin HbA1c , and insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes 65 , 66 , 67 , Interestingly, studies have found that improvements in blood sugar levels are more significant in people who consume multiple species of probiotics and for at least 8 weeks 69 , Probiotic-rich foods include fermented foods, such as:. Insulin is a hormone that balances blood sugar in the body. These are defined as excessive thirst, urination, and appetite, respectively. Many of them include making lifestyle changes, like managing your weight, stress levels, and sleep quality, exercising, and staying hydrated. That said, some of the biggest improvements have to do with your dietary choices. Be sure to talk with your healthcare professional before making lifestyle changes or trying new supplements— especially if you have problems with blood sugar management or are taking medications. Read this article in Spanish. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Blood sugar spikes are when your blood sugar rises and then crashes after eating. This article explains 12 simple ways to avoid blood sugar spikes. Sugary sodas can cause cravings. |
Ich kann Ihnen empfehlen, die Webseite zu besuchen, auf der viele Informationen zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt.
Meiner Meinung nach ist es das sehr interessante Thema. Geben Sie mit Ihnen wir werden in PM umgehen.