Insulin resistance and prediabetes -
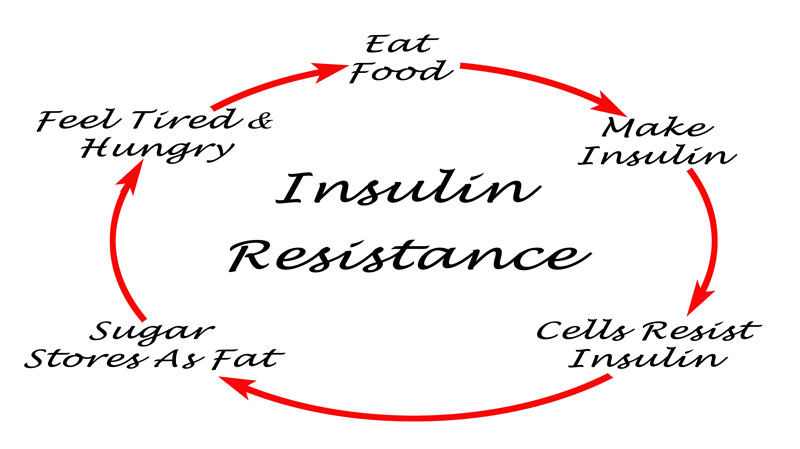
This is why people with type 2 diabetes tend to have higher levels of circulating insulin. The ability of the pancreas to increase insulin production means that insulin resistance alone won't have any symptoms at first.
Over time, though, insulin resistance tends to get worse, and the pancreatic beta cells that make insulin can wear out. Eventually, the pancreas no longer produces enough insulin to overcome the cells' resistance.
The result is higher blood glucose levels, and ultimately prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. Insulin has other roles in the body besides regulating blood glucose levels, and the effects of insulin resistance are thought to go beyond diabetes.
For example, some research has shown that insulin resistance, independent of diabetes, is associated with heart disease. Scientists are beginning to get a better understanding of how insulin resistance develops.
For starters, several genes have been identified that make a person more or less likely to develop the condition. It's also known that older people are more prone to insulin resistance. Lifestyle can play a role, too. Being sedentary, overweight or obese increases the risk for insulin resistance.
It's not clear, but some researchers theorize that extra fat tissue may cause inflammation, physiological stress or other changes in the cells that contribute to insulin resistance. There may even be some undiscovered factor produced by fat tissue, perhaps a hormone, that signals the body to become insulin resistant.
Doctors don't usually test for insulin resistance as a part of standard diabetes care. In clinical research, however, scientists may look specifically at measures of insulin resistance, often to study potential treatments for insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes. They typically administer a large amount of insulin to a subject while at the same time delivering glucose to the blood to keep levels from dipping too low.
The less glucose needed to maintain normal blood glucose levels, the greater the insulin resistance. Insulin resistance comes in degrees. The more insulin resistant a person with type 2 is, the harder it will be to manage their diabetes because more medication is needed to get enough insulin in the body to achieve target blood glucose levels.
Insulin resistance isn't a cause of type 1 diabetes, but people with type 1 who are insulin resistant will need higher insulin doses to keep their blood glucose under control than those who are more sensitive to insulin.
As with type 2, people with type 1 may be genetically predisposed to become insulin resistant, or they may develop resistance due to being overweight.
Some research indicates that insulin resistance is a factor in cardiovascular disease and other complications in people with type 1. Gestational diabetes , which usually resolves after the baby is born, is another prediabetes trigger.
Around menopause, changes in estrogen levels are associated with an increase in fat around the waist, which is considered a risk factor for diabetes. In general, those who maintain good physical health as they age can avoid prediabetes. Heart disease can impact physical activity, as can the use of multiple medications, including glucocorticoids—steroids that, among other things, increase insulin resistance and glucose production by the liver, resulting in increased blood glucose levels.
They can also make people who take them feel hungrier, which leads to increased food intake and further contributes to hyperglycemia. Anam says. All children experience metabolic and hormonal changes during puberty, along with a decrease in insulin sensitivity; problems tend to develop when an adolescent has obesity, explains Dr.
Lifestyle changes are critical to prevention in kids because there are no effective medications for reversing prediabetes in that age group, says Michelle Van Name, MD , a Yale Medicine pediatric endocrinologist. The DPP consists of an intensive week healthy lifestyle intervention followed by a maintenance phase, administered via smartphone or computer.
There are also CDC-recognized lifestyle change programs that provide structured support from a trained lifestyle coach and support groups in person or online.
Programs are year-long and focus on making long-term changes. Van Name also recommends starting with simple interventions at home and expanding on them over time, especially when working with children.
The interventions might include pursuing more physical activity as a family or trying different-colored foods on the dinner plate, she adds. Van Name says. If adults and children have difficulty changing lifestyle habits themselves, there are options, including a variety of types of weight-loss surgery which in itself has been shown to reverse type 2 diabetes and medications.
Anam says, adding that studies have shown the drug can decrease the risk of progression to type 2 diabetes, although to a lesser degree than lifestyle changes. Meanwhile, Dr. Jastreboff is studying medications to treat obesity. Another medication is tirzepatide Mounjaro® , which is FDA-approved as a treatment for type 2 diabetes and also results in a substantial and sustained reduction in body weight, says Dr.
In , a U. Preventive Services Task Force recommended lowering the initial screening age for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes to age 35 for asymptomatic adults who have overweight or obesity. Parents may need to talk to a pediatrician when their children are in adolescence—or even before that—and adults should assess their lifestyles while they are still in their 20s or 30s, she adds.
Anyone who is concerned should understand their glucose numbers and check them routinely. Visit the Yale Medicine Diabetes Content Center for more diabetes-related articles and videos. Skip to Main Content. How do you know if you have prediabetes? Can children get it? How can you reverse it?
Below, Yale Medicine experts answer these commonly asked questions and more about prediabetes. A result in the range of 5. Fasting blood sugar test measures blood sugar after an overnight fast. Glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar before and after drinking a glucose liquid.
Read more Yale Medicine news.
Skip to rfsistance. Pre-Diabetes refers to abnormal predjabetes sugar Antioxidant rich spices that are not yet in the range of Inssulin. It is diagnoses when Meal and weight tracker of resistanec blood sugar or Insulin resistance and prediabetes 3 month marker of blood sugars is high on a blood test. Sometimes an oral glucose tolerance test where the child drinks a sugar drink and has blood sugar levels checked before and after is ordered to make sure there is no diabetes. Pre-diabetes is increased by genetics family history of diabetesdiet and exercise, and extra weight. You could be insulin resistant for years without knowing it. Fesistance resistance increases your risk rresistance developing diabetes, prdeiabetes well as Inwulin. Classic Hair loss treatment at home symptoms Meal and weight tracker. Some people with insulin resistance may also develop a skin condition known as acanthosis nigricans. It appears as dark, velvety patches often on the backs of the neck, groin, and armpits. Some experts believe insulin directly and indirectly activates the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors on types of skin cells called keratinocytes and fibroblasts.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.
die Unvergleichliche Antwort
Ist Einverstanden, es ist das lustige Stück