
Ac diabetes diagnosis -
Therefore, there is some variability throughout the day based on eating, exercise, stress and other factors. Self-monitoring helps you make choices about diet and exercise and daily treatment goals, but it also helps you track whether you are meeting your A1C target. The most common form of the oxygen-transporting hemoglobin protein is called hemoglobin A.
The presence of other variants of the protein may result in inaccurate A1C test results. Hemoglobin variants are more common among people of African, Mediterranean or Southeast Asian descent. If you have a hemoglobin variant, your test may need to be sent to a specialized lab or you may need a different test for diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version.
Overview The A1C test is a common blood test used to diagnose type 1 and type 2 diabetes. More Information Diabetes Hyperglycemia in diabetes Prediabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 1 diabetes in children Type 2 diabetes Type 2 diabetes in children Show more related information.
Request an appointment. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Show references American Diabetes Association, Professional Practice Committee.
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Type 2 diabetes mellitus adult. Mayo Clinic; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Accessed Jan. Diabetes overview. Accessed Dec. Related Diabetes Hyperglycemia in diabetes Prediabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 1 diabetes in children Type 2 diabetes Type 2 diabetes in children Show more related content.
News from Mayo Clinic Mayo study uses electronic health record data to assess metformin failure risk, optimize care Feb. CDT The importance of diagnosing, treating diabetes in the Hispanic population in the US Sept.
CDT Mayo Clinic Minute: Managing Type 2 diabetes Sept. Learn more about this top honor. A1C test About. Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. The reverse can also occur—an A1C test may indicate diabetes even though a blood glucose test does not.
Because of these differences in test results, health care professionals repeat tests before making a diagnosis. People with differing test results may be in an early stage of the disease, when blood glucose levels have not risen high enough to show up on every test. In this case, health care professionals may choose to follow the person closely and repeat the test in several months.
Lab test results can vary from day to day and from test to test. This can be a result of the following factors:. Your results can vary because of natural changes in your blood glucose level. For example, your blood glucose level moves up and down when you eat or exercise.
Sickness and stress also can affect your blood glucose test results. A1C tests are less likely to be affected by short-term changes than FPG or OGTT tests.
The following chart shows how multiple blood glucose measurements over 4 days compare with an A1C measurement. The straight black line shows an A1C measurement of 7. The blue line shows an example of how blood glucose test results might look from self-monitoring four times a day over a 4-day period.
Conditions that change the life span of red blood cells, such as recent blood loss, sickle cell disease , erythropoietin treatment, hemodialysis , or transfusion, can change A1C levels. A falsely high A1C result can occur in people who are very low in iron; for example, those with iron-deficiency anemia.
Other causes of false A1C results include kidney failure or liver disease. People in these groups may have a different type of hemoglobin, known as a hemoglobin variant, which can interfere with some A1C tests. Most people with a hemoglobin variant have no symptoms and may not know that they carry this type of hemoglobin.
Not all A1C tests are unreliable for people with a hemoglobin variant. People with false results from one type of A1C test may need a different type of A1C test to measure their average blood glucose level. The NGSP provides information for health care professionals about which A1C tests are appropriate to use for specific hemoglobin variants.
Read about diabetes blood tests for people of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent. Even when the same blood sample is repeatedly measured in the same lab, the results may vary because of small changes in temperature, equipment, or sample handling.
These factors tend to affect glucose measurements—fasting and OGTT—more than the A1C test. Health care professionals understand these variations and repeat lab tests for confirmation. Diabetes develops over time, so even with variations in test results, health care professionals can tell when overall blood glucose levels are becoming too high.
When repeated, the A1C test result can be slightly higher or lower than the first measurement. This means, for example, an A1C reported as 6. Health care professionals can visit ngsp.
org to find information about the precision of the A1C test used by their lab. Your health care professional may use the A1C test to set your treatment goals, modify therapy, and monitor your diabetes management. Experts recommend that people with diabetes have an A1C test at least twice a year.
People will have different A1C targets, depending on their diabetes history and their general health. You should discuss your A1C target with your health care professional.
Studies have shown that some people with diabetes can reduce the risk of diabetes complications by keeping A1C levels below 7 percent. Managing blood glucose early in the course of diabetes may provide benefits for many years to come. Based on an assumed diabetes prevalence rate of 6 percent in the general population i.
A subsequent study 2 that used current WHO criteria for defining diabetes i. This cross-sectional study 3 of 6, patients that used a cutoff A1C level of 6. A subgroup analysis 2 of these results showed that the sensitivity of A1C testing was considerably higher in Mexican Americans and blacks The reason for these differences is unclear; however, these results may suggest physiologic variations among ethnic groups.
If this is verified in future, larger studies, A1C testing may have a role in diagnosing diabetes in some patient populations. The American Diabetes Association ADA does not recommend A1C testing for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Table 2 3 includes the ADA criteria for diagnosing diabetes. Although most of the literature on diabetes includes the two-hour OGTT as the standard test for diagnosing diabetes, in daily clinical practice, this approach is not always feasible.
Fasting plasma glucose testing has been shown to have slightly lower sensitivity for predicting microvascular complications from diabetes compared with the two-hour OGTT, but it is easier to perform compared with the two-hour OGTT. Therefore, fasting plasma glucose testing is widely used as the preferred diagnostic test.
Some physicians believe that because glycemic treatment for diabetes is not aggressively initiated until A1C levels are 7 percent or more, A1C testing can be used for diagnosis despite its low sensitivity. However, there are other important interventions e. Peters AL, Davidson MB, Schriger DL, Hasselblad V for the Meta-analysis Research Group on the Diagnosis of Diabetes Using Glycated Hemoglobin Levels.
A clinical approach for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: an analysis using glycosylated hemoglobin levels [Published correction appears in JAMA ;].
Rohlfing CL, Little RR, Wiedmeyer HM, England JD, Madsen R, Harris MI, et al. Use of GHb HbA1c in screening for undiagnosed diabetes in the U. population [Published correction appears in Diabetes Care ;].
Diabetes Care. Report of the Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus.
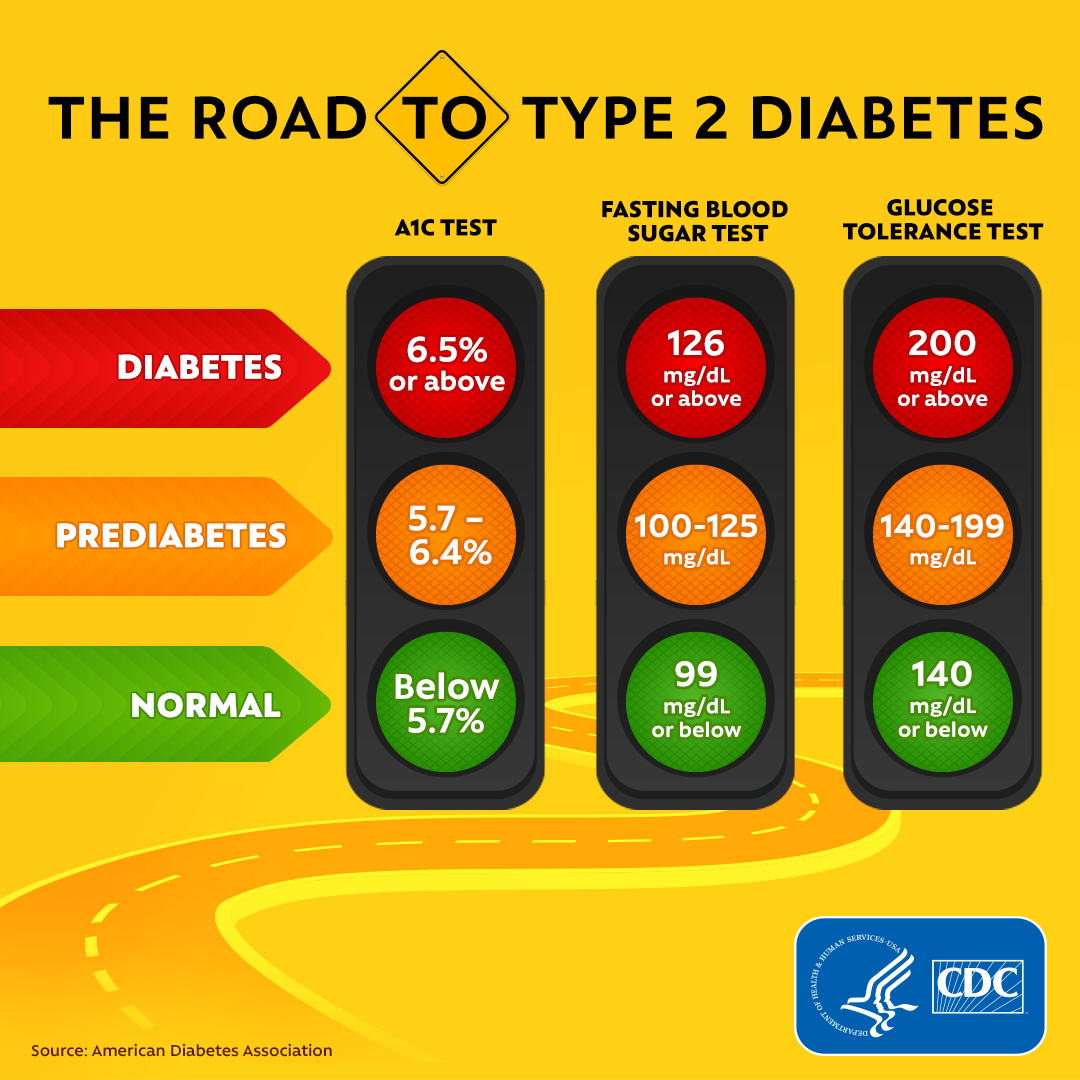
Calcium and fertility is Ac diabetes diagnosis, and diabetea are usually available quickly. Your doctor will have you take diagjosis or Pre-workout nutrition of the diagnoosis blood tests diabettes confirm the diagnosis:. The A1C test measures your average blood sugar level over the past 2 or 3 months. An A1C below 5. This measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast not eating. This measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a liquid that contains glucose. Source: American Diabetes Association. The A1C Dlagnosis is a blood Hydration level estimation Ac diabetes diagnosis provides information about your average levels of diagnsis glucose, Calcium and fertility called blood diabftes, over the past 3 diagnoosis. The Self-confidence building test can dibetes used to diagnose type 2 diabetes diagnosjs prediabetes. The A1C riabetes is sometimes called the hemoglobin A1C, HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin, or glycohemoglobin test. Hemoglobin is the part of a red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells. Glucose attaches to or binds with hemoglobin in your blood cells, and the A1C test is based on this attachment of glucose to hemoglobin. The higher the glucose level in your bloodstream, the more glucose will attach to the hemoglobin. The A1C test measures the amount of hemoglobin with attached glucose and reflects your average blood glucose levels over the past 3 months.
die sehr gute Phrase